Opinion|Videos|May 1, 2025
Case 1: Managing Suboptimal Response in Bilateral nAMD: Transitioning From Biosimilars to High-Dose Aflibercept for Durable Drying
Author(s)Michael A. Klufas, MD
A panelist discusses how a woman aged 74 years with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) showed improved disease control and vision in her right eye after switching from ranibizumab to a high-dose aflibercept (8 mg) treatment that successfully extended intervals to 10 weeks.
Advertisement
Clinical Brief: Aflibercept 8 mg for nAMD
Main Discussion Topics
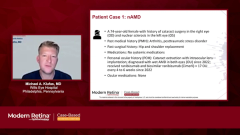
- Treatment Response and Switching Therapies: A woman aged 74 years with suboptimal control of nAMD in the right eye despite 17 injections of ranibizumab/biosimilar, whereas the left eye showed good control.
- High-Dose Aflibercept Initiation: Decision to start aflibercept 8 mg for better disease control and potential treatment interval extension in both eyes.
- Extended Treatment Intervals: Patient demonstrated improved disease control with aflibercept 8 mg, allowing successful extension from 6 weeks to 8 weeks and eventually 10 weeks between treatments.
- Long-term Response Patterns: Vision improved over time with continued reduction in central subfield thickness, even with extended treatment intervals.
Key Points for Physicians
- Patients may show improved disease control over time with extended treatment intervals of aflibercept 8 mg.
- Residual edema or subretinal fluid does not necessarily require reducing treatment intervals if vision remains stable and no hemorrhage is present.
- Treatment extension to 8 to 10 weeks was possible while maintaining disease control.
- Consider patient preferences and treatment burden when selecting the treatment agent and intervals.
Notable Insights
- Some physicians prefer using the same agent in both eyes, even with differential response.
- Clinicians may have varying tolerance for subretinal vs intraretinal fluid.
- No specific demographic or optical coherence tomography features reliably predicted superior response to particular agents.
- Determining nonresponse vs lack of durability remains challenging, with some patients potentially requiring very frequent anti-VEGF suppression.
Clinical Significance
The case demonstrates that aflibercept 8 mg offers effective disease control for nAMD with the potential for extended treatment intervals, reducing treatment burden while maintaining visual outcomes.
Newsletter
Keep your retina practice on the forefront—subscribe for expert analysis and emerging trends in retinal disease management.
Advertisement
Latest CME
Advertisement
Advertisement