
Delaying the disease can also delay any onset of vision problems, including diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema.

Singapore investigators discover novel therapeutic target to advance treatment of diabetic eye diseases

Delaying the disease can also delay any onset of vision problems, including diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema.
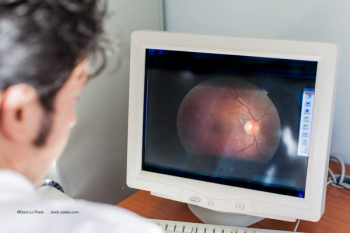
Being able to visualize and evaluate the retinal periphery provides a better understanding of the disease status and supports a better treatment decision.
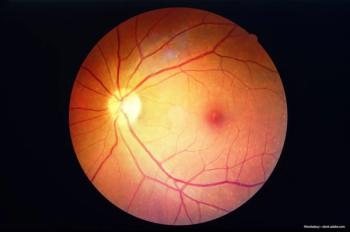
An end-of-week review of retina news and stories from October 29-November 3, 2022.

RGX-314 is being investigated as a potential one-time treatment for wet AMD, diabetic retinopathy, and other chronic retinal conditions.
Data highlights need for educational materials and training resources in DME and DR.

A combination of posters, podium presentations, and instructional courses provided invaluable revelations to the ophthalmic community.
The investigators emphasized that hydroxychloroquine doses of 5 mg/kg/day or less, in accordance with current ophthalmology and rheumatology guidelines, was associated with a higher risk of lupus flares, and the threshold was near 5 mg/kg/day.

Oral APX3330 was found to demonstrate favorable safety and tolerability profile in interim masked safety results, consistent with 11 prior trials of APX3330.

The Phase 2 Altitude study is an open-label, randomized, controlled, dose-escalation evaluation of RGX-314, evaluating the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of suprachoroidal delivery of RGX-314 in patients with moderately severe/severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy or mild proliferative diabetic retinopathy.

This year’s hybrid meeting will allow attendees to participate in person or virtually. Either way, this congress will offer a wealth of information to specialists covering all aspects of retinal diseases.

Nancy Lurker, CEO of EyePoint Pharmaceuticals, shares the 12-month safety data from the DAVIO trial, investigating EYP-1901 for the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy.
While the COVID-19 pandemic revealed the potential of utilizing artificial intelligence in screening for diabetic retinopathy, improvements are still needed as a results of the number of images that are ungradable.
A team of scientists, led by Andrzej Foik, PhD, of the International Center for Translational Eye Research, is working on new therapies that may slow vision loss in patients diagnosed with retinal degeneration.

Kerrie Brady, CEO of OcuTerra Therapeutics, shares an update on their eye drop-based integrin inhibitor, which is intended to be a novel therapy for diabetic retinopathy.

The ASRS "See for a Lifetime; See a Retina Specialist" initiative will spotlight early detection and outline the importance of seeing a retina specialist.

The future risk of the development of new-onset vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy can be predicted using the patient’s retinopathy status and hemoglobin A1c value.
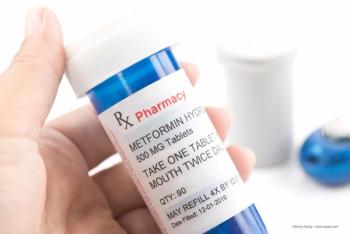
Metformin, a frequently prescribed drug to treat diabetes, could be a novel therapy for AMD.

Dr. Diana Do presents data on a novel patient-reported outcome instrument for patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy with the hope of capturing the burden of the disease and treatment.
According to an e-poster presented by Jagadesh C. Reddy, MD, and Harini Indusekar, BScOptom, at the ASCRS in Washington, D.C., patients who have pre-existing DR are less likely to achieve Snellen 20/40 or better vison after cataract surgery compared with the patients with diabetes but without DR.

The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology’s 2022 annual meeting in Denver, Colorado, revealed a variety of advancements in technology, pivotal trials and clinical trial design.

Dr. David Bingaman of Ora Clinical discusses today’s need to accelerate clinical studies and increase investments in retina and challenging disease states.

According to review, patients with mild diabetic retinopathy at baseline fare better.
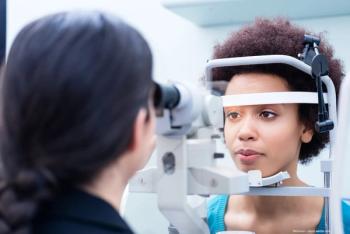
A University of Houston study found that minorities have fewer eye exams, higher instances of disease.

Leading the charge for a multifactorial approach to combat diabetes, Kristen Nwanyanwu, MD, MBA, MHS, and her team have embraced the need for a multi-pronged program to address health disparities in diabetic retinopathy.

Dr. Quan Dong Nguyen reviews a Monte Carlo simulation that showed evidence that treating severe NPDR with anti-VEGF therapy garners positive results.