Post hoc analysis: Protocol V provides more practical DME guidance for clinicians
Three risk-related baseline factors identified by this analysis may be associated with a potential need for injections.

Three risk-related baseline factors identified by this analysis may be associated with a potential need for injections.

A study including data from about 42,000 eyes found diabetic retinopathy (DR) severity is a risk factor for the progression of diabetic eye disease. Other findings support the idea that genetic factors influence the development of proliferative DR versus diabetic macular edema.

Study highlights the role of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics as contributors to disease- and treatment-related disparities among patients with diabetic macular edema.





Ehsan Rahimy, MD, speaks on the highlights of a study he presented at this year's virtual AAO 2020 meeting that aimed to integrate an artificial intelligence screening system for managing diabetic retinopathy referrals in a primary care setting — with limited specialty support.

A panel of experts in ophthalmology and optometry review the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic eye disease including emerging agents in the field.

Results support further research investigating transforming growth factor-β-Induced Gene Human Clone 30 (BIGH3).
The benefit is robust across a variety of demographics and baseline disease characteristics, according to data.

Study offers a real-world scenario of a very specific, but frequent and crucial aspect of the care of patients with diabetes, suggests clinician
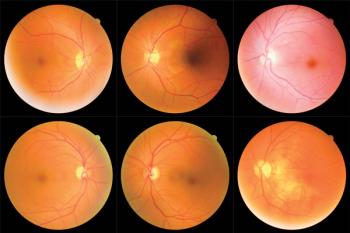
Visual acuity outcomes at 6 months’ post-treatment were similar, regardless of the use of anti-VEGF therapy.
Results could provide a new preferred treatment paradigm for this population

Study explores correlations between functional and structural tests

The number of patients with retinal diseases is steadily increasing in the United States, according to a retrospective study presented during ARVO 2020.
Reductions in macular retinal nonperfusion after anti-VEGF treatment with aflibercept are correlated with improvements in BCVA and central retinal thickness in patients with DR/DME, according to a post-hoc analysis of the VISTA dataset, said Charles C. Wykoff, MD, PhD, during ARVO 2020.
Caesar Luo, MD, shares the take-away points from his ASRS presentation, and how the topics from his talk may be applied day to day in retinal practice.

Rates of anxiety and depression increased but were not necessarily tied to disease severity

A retrospective study found that in both patients with type 2 diabetes and non-diabetics, average central macular thickness was lower in Asians than Caucasians. Why is this significant for clinicians?